「格物志 玖」用动图理解CNN卷积神经网络的前向反向传播
Convolutional Neural Network
Image Classification & Feature Extraction
Principle
本库使用CIFAR10数据集,只实现了简单的CNN,其余高级variants详见
(包含VGG, Resnet, MobileNet, Googlenet, EfficientNet, Densenet, Shufflenet, Regnet, DPN)
因为 CNN 开始就不再是 sklearn 的范围了,我寻思着加一个tensorflow的原生版本吧。Guess what? 相比于keras和pytorch,这简直是地狱级难度! 拥有keras和pytorch真是件幸运的事。我甚至觉得比我自己写的都麻烦,大家自己对比一下各个类的代码长度吧,都放在models.py里了。
- Skylark_CNN
- Keras_CNN
- Torch_CNN
- TF_CNN
Trust me! Do not use TF for the beginning!
CNN的主体就是卷积+池化+全连接三步,self-implement简单地构建了一层卷积池化全连接,如果需要更多可以像keras和pytorch一样加层。实测mnist训练集可以达到100%,CIFAR10有些勉强emmm。
注:
- 全连接这里写的不是很好,需要改class,待修改,
- batch也没有加入,现在还是batch=1,TODO
- 欢迎contribute。
self.conv2d = Conv3x3(8) # 32x32x1 -> 30x30x8
self.pool = MaxPool2() # 30x30x8 -> 15x15x8
self.softmax = Softmax(15 * 15 * 8, 10) # 15x15x8 -> 10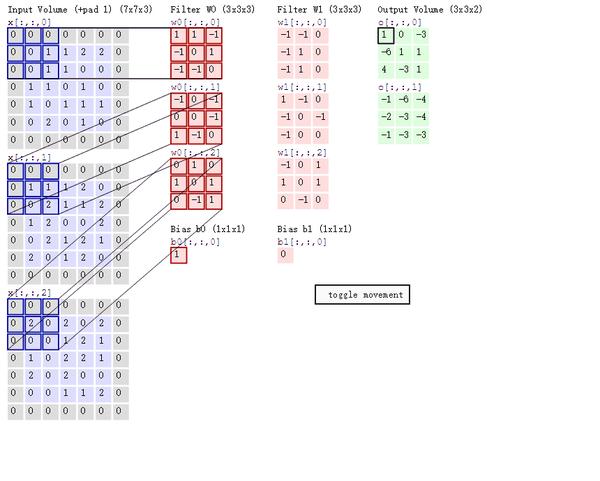
Convolution
def iterate_regions(self, image):
'''
Generates all possible 3x3 image regions using valid padding.
- image is a 2d numpy array.
'''
h, w = image.shape
for i in range(h - 2):
for j in range(w - 2):
im_region = image[i:(i + 3), j:(j + 3)]
yield im_region, i, j
def forward(self, input):
'''
Performs a forward pass of the conv layer using the given input.
Returns a 3d numpy array with dimensions (h, w, num_filters).
- input is a 2d numpy array
'''
self.last_input = input
h, w = input.shape
output = np.zeros((h - 2, w - 2, self.num_filters))
for im_region, i, j in self.iterate_regions(input):
output[i, j] = np.sum(im_region * self.filters, axis=(1, 2))
return output- 设计一个生成器用于从图像上切割与卷积核相同大小的图像块;
- 卷积后的输出尺寸是(h - 2, w - 2, self.num_filters),这里未考虑补零padding操作,所以会有边缘缺失;
- 对于output的每一个z轴,是一个长度为self.num_filters=8的数组,
np.sum(im_region * self.filters, axis=(1, 2))将 3x3 矩阵与8个 3x3 的滤波器乘在一起得到一个8x3x3的矩阵,再对第二、三维求和,即得长度为8的数组。
Maxpool
def iterate_regions(self, image):
'''
Generates non-overlapping 2x2 image regions to pool over.
- image is a 2d numpy array
'''
h, w, _ = image.shape
new_h = h // 2
new_w = w // 2
for i in range(new_h):
for j in range(new_w):
im_region = image[(i * 2):(i * 2 + 2), (j * 2):(j * 2 + 2)]
yield im_region, i, j
def forward(self, input):
'''
Performs a forward pass of the maxpool layer using the given input.
Returns a 3d numpy array with dimensions (h / 2, w / 2, num_filters).
- input is a 3d numpy array with dimensions (h, w, num_filters)
'''
self.last_input = input
h, w, num_filters = input.shape
output = np.zeros((h // 2, w // 2, num_filters))
for im_region, i, j in self.iterate_regions(input):
output[i, j] = np.amax(im_region, axis=(0, 1))
return output- 这里用的是2x2最大池化,因此要从上一步的输出中制作一个生成器来生成所有2x2大小的下图像块;
- 2x2最大池化后的输出是原长宽的一半,(h / 2, w / 2, num_filters);
- output的每一个z向量是这个2x2图像块中值最大的那一个。
Softmax
def forward(self, input):
'''
Performs a forward pass of the softmax layer using the given input.
Returns a 1d numpy array containing the respective probability values.
- input can be any array with any dimensions.
'''
self.last_input_shape = input.shape
input = input.flatten()
self.last_input = input
input_len, nodes = self.weights.shape
totals = np.dot(input, self.weights) + self.biases
self.last_totals = totals
exp = np.exp(totals)
return exp / np.sum(exp, axis=0)- 这里的softmax包含了全连接输出层;
- 先将上一步的output展平
input = input.flatten(); - 经过一层全连接
totals = np.dot(input, self.weights) + self.biases; - softmax激活函数
exp = np.exp(totals); exp / np.sum(exp, axis=0); - 得到其属于各个类别的可能性,这是一个长度为10的数组,之后会使用argmax作为最终预测的类别。
Backpropagation
当然是 全连接->池化->卷积
Softmax backprop
def backprop(self, d_L_d_out, learn_rate):
'''
Performs a backward pass of the softmax layer.
Returns the loss gradient for this layer's inputs.
- d_L_d_out is the loss gradient for this layer's outputs.
- learn_rate is a float.
'''
# We know only 1 element of d_L_d_out will be nonzero
for i, gradient in enumerate(d_L_d_out):
if gradient == 0:
continue
# e^totals
t_exp = np.exp(self.last_totals)
# Sum of all e^totals
S = np.sum(t_exp)
# Gradients of out[i] against totals
d_out_d_t = -t_exp[i] * t_exp / (S ** 2)
d_out_d_t[i] = t_exp[i] * (S - t_exp[i]) / (S ** 2)
# Gradients of totals against weights/biases/input
d_t_d_w = self.last_input
d_t_d_b = 1
d_t_d_inputs = self.weights
# Gradients of loss against totals
d_L_d_t = gradient * d_out_d_t
# Gradients of loss against weights/biases/input
d_L_d_w = d_t_d_w[np.newaxis].T @ d_L_d_t[np.newaxis]
d_L_d_b = d_L_d_t * d_t_d_b
d_L_d_inputs = d_t_d_inputs @ d_L_d_t
# Update weights / biases
self.weights -= learn_rate * d_L_d_w
self.biases -= learn_rate * d_L_d_b
return d_L_d_inputs.reshape(self.last_input_shape)全连接的反向传播我们在上一章NN已经研究过了,这里大家看看代码就熟悉了。
Maxpool backprop
def backprop(self, d_L_d_out):
'''
Performs a backward pass of the maxpool layer.
Returns the loss gradient for this layer's inputs.
- d_L_d_out is the loss gradient for this layer's outputs.
'''
d_L_d_input = np.zeros(self.last_input.shape)
for im_region, i, j in self.iterate_regions(self.last_input):
h, w, f = im_region.shape
amax = np.amax(im_region, axis=(0, 1))
for i2 in range(h):
for j2 in range(w):
for f2 in range(f):
# If this pixel was the max value, copy the gradient to it.
if im_region[i2, j2, f2] == amax[f2]:
d_L_d_input[i * 2 + i2, j * 2 + j2, f2] = d_L_d_out[i, j, f2]
return d_L_d_input利用self.last_input来找出最大值的位置,请将其还原到池化前的尺寸。

Conv backprop
def backprop(self, d_L_d_out, learn_rate):
'''
Performs a backward pass of the conv layer.
- d_L_d_out is the loss gradient for this layer's outputs.
- learn_rate is a float.
'''
d_L_d_filters = np.zeros(self.filters.shape)
for im_region, i, j in self.iterate_regions(self.last_input):
for f in range(self.num_filters):
d_L_d_filters[f] += d_L_d_out[i, j, f] * im_region
# Update filters
self.filters -= learn_rate * d_L_d_filters
# We aren't returning anything here since we use Conv3x3 as the first layer in our CNN.
# Otherwise, we'd need to return the loss gradient for this layer's inputs, just like every
# other layer in our CNN.
return None卷积前向传播:


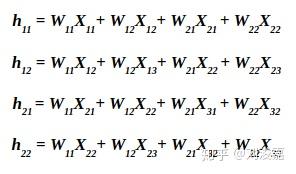
卷积反向传播:
这里用 \partial h_{ij} 代表 \frac{\partial L}{\partial h_{ij}} ,用 \partial w_{ij} 代表 \frac{\partial L}{\partial w_{ij}}

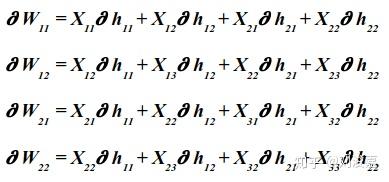
self.last_input就是Xd_L_d_out就是 \frac{\partial L}{\partial h_{ij}}d_L_d_filters[f] += d_L_d_out[i, j, f] * im_region就是第f个滤波器的3x3的 \partial w 。
更多实现方式见本专栏关联Github
Reference
编辑于 2020-05-05 12:52

